verilog 10 FSM/ASM
2023. 3. 17. 18:44ㆍVerilog
FSM : 지정된 수의 상태로 상태들 과의 천이에 의해 출력을 생성하는 회로
디지털 시스템의 제어회로 구성에 사용
무어 머신(Moore Machine) : 출력이 현재상태에 의해서만 결정, 동기형 출력
밀리 머신(Mealy Machine) : 출력이 현재상태와 입력에 의해서만 결정, 비동기형 출력
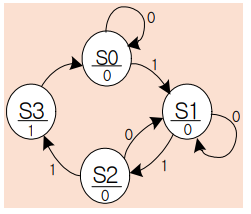
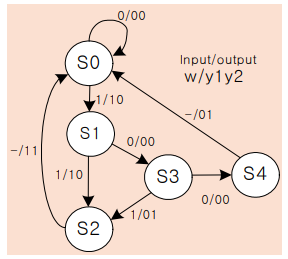
FSM은 보통 3부분으로 구성된다.
- 현재상태를 기억하는 레지스터
- 다음상태를 계산하는 논리회로(조합회로)
- 현재 출력을 계산하는 조합회로
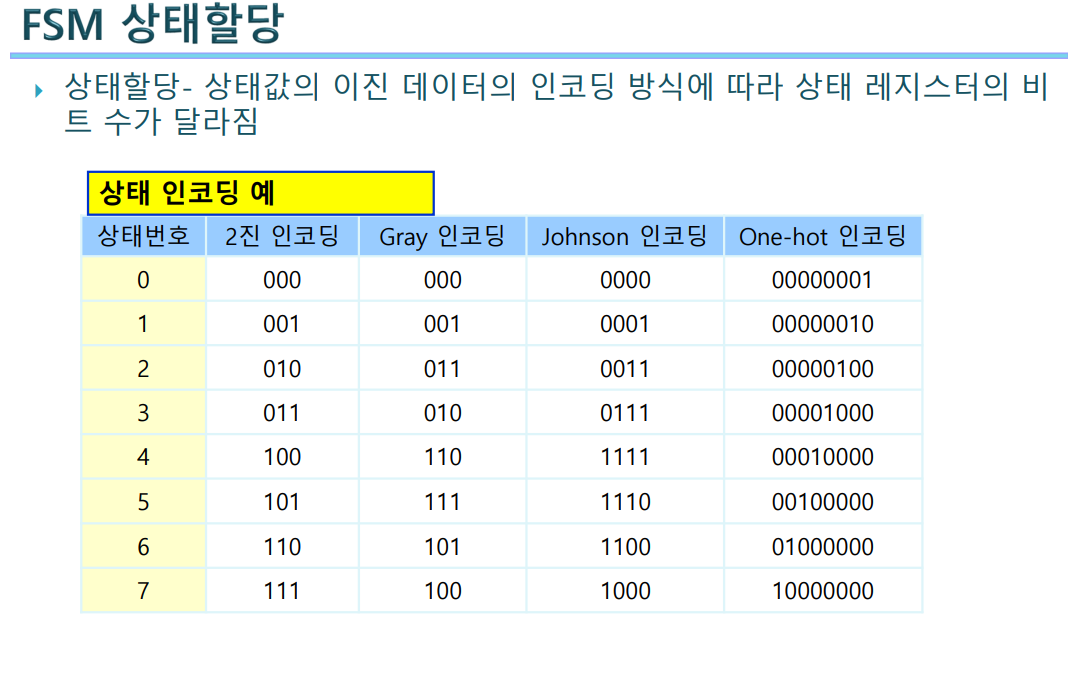
FSM의 코딩 가이드라인
- FSM의 상태 이름을 Parameter 또는 localParam으로 정의해서 사용한다.
module fsm_v1(
input clk, rst, x,
output reg y
);
localparam [1:0] S0 = 2’b00, S1 = 2’b01, S2 = 2’b10, S3 = 2’b11 ;
reg [1:0] curr_st, nx_st;
...
endmodule- FSM이 비동기 리셋을 할 수 있게 설계한다. 리셋을 갖지 않으면 초기상태가 미정의되어 오류가 발생할 수 있다.
- FSM을 구성하는 3개의 블록(다음상태, 현재 상태 레지스터, 출력)을 분리된 always 또는 assign문으로 구현한다.
- 상태 레지스터는 플리플롭을 사용한다.
- 다음상태 logic은 case문을 사용하고, 정의되지 않은 상태들은 default문으로 표현하고, 외부 입력은 case문에서 if~else를 사용한다.
무어머신
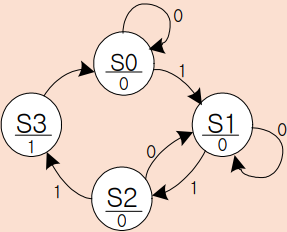
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module Moore(
input clk, rst, x,
output reg y
);
reg y_temp;
reg [1:0] next_state, curr_state;
localparam S0 = 2'b00, S1 = 2'b01, S2 = 2'b10, S3 = 2'b11;
always @(posedge clk , posedge rst) begin
if(rst) curr_state <= S0;
else curr_state <= next_state;
end
always @(curr_state, x) begin
case(curr_state)
S0 : if(x) next_state = S1; else next_state = S0;
S1 : if(x) next_state = S2; else next_state = S0;
S2 : if(x) next_state = S3; else next_state = S1;
S3 : next_state = S0;
default : next_state = S0;
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk,posedge rst) begin
if(rst)
y<= 0;
else
y<= y_temp;
end
always @(*) begin
if(next_state == S3)
y_temp = 1'b1;
else
y_temp = 1'b0;
end
endmodule
밀리머신
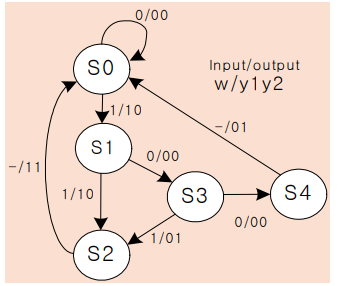
module mealy (
input clk, rst, w,
output reg [1:0] y
);
reg [2:0] curr_state, next_state;
localparam [2:0] S0 = 3'd0, S1 = 3'd1, S2 = 3'd2, S3 = 3'd3, S4 = 3'd4;
always @(posedge clk , posedge rst) begin
if(rst) curr_state <= S0;
else curr_state <= next_state;
end
always @(curr_state, w) begin
y = 2'b00;
case(curr_state)
S0 :
if(w) begin
y = 2'b10; next_state = S1;
end
else begin
y = 2'b00; next_state = S0;
end
S1 :
if(w) begin
y = 2'b10; next_state = S2;
end
else begin
y = 2'b00; next_state = S3;
end
S2 :
begin
y=2'b11; next_state = S0;
end
S3 :
if(w) begin
y = 2'b01; next_state = S2;
end
else begin
y = 2'b00; next_state = S4;
end
S4 :
begin
y=2'b01; next_state = S0;
end
default : next_state = S0;
endcase
end
endmodule
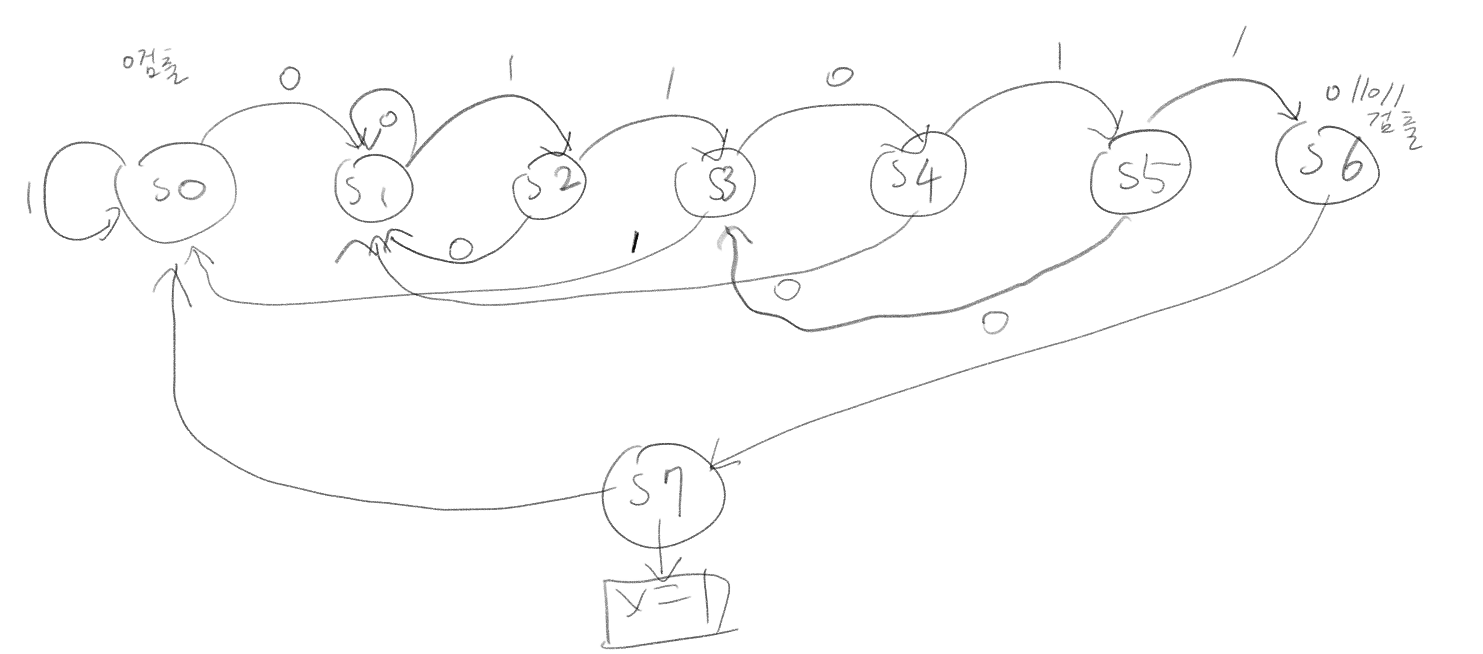
패턴 검출(011011)
module pattern_detect (
input clk, rst, x,
output reg y
);
localparam [3:0] S0 = 3'd0, S1 = 3'd1, S2 = 3'd2, S3 = 3'd3, S4 = 3'd4, S5 = 4'd5, S6 = 4'd6, S7 = 3'd7;
reg[2:0] curr_state, next_state;
always @(posedge clk, posedge rst) begin
if(rst) curr_state <= 0;
else curr_state <= next_state;
end
always @(x, curr_state) begin
case (curr_state)
S0 :
if(x) next_state = S0;
else next_state = S1;
S1 :
if(x) next_state = S2;
else next_state = S1;
S2:
if(x) next_state = S3;
else next_state = S1;
S3 :
if(x) next_state = S1;
else next_state = S4;
S4 :
if(x) next_state = S5;
else next_state = S1;
S5 :
if(x) next_state = S6;
else next_state = S3;
S6 : next_state = S7;
S7 : next_state = S0;
default: next_state = S0;
endcase
end
always @(*) begin
if(next_state == S7) y <= 1'b1;
else y <= 1'b0;
end
endmodule011011이 들어오면 출력으로 1이 나오는 코드이다.
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module tb_pattern;
parameter WD = 30;
reg clk, rst;
reg in;
reg [0:WD-1] arr = 30'b0001_0011_0101_1101_0110_1011_0110_10;
integer i;
wire y;
pattern_detect u1(.clk(clk), .rst(rst), .x(in), .y(y));
initial begin
clk = 0; rst = 1; in = 0;
#50 rst = 0;
for(i=0; i<WD; i=i+1) begin
#10 in = arr[i];
end
end
always #5 clk = ~clk;
endmodule
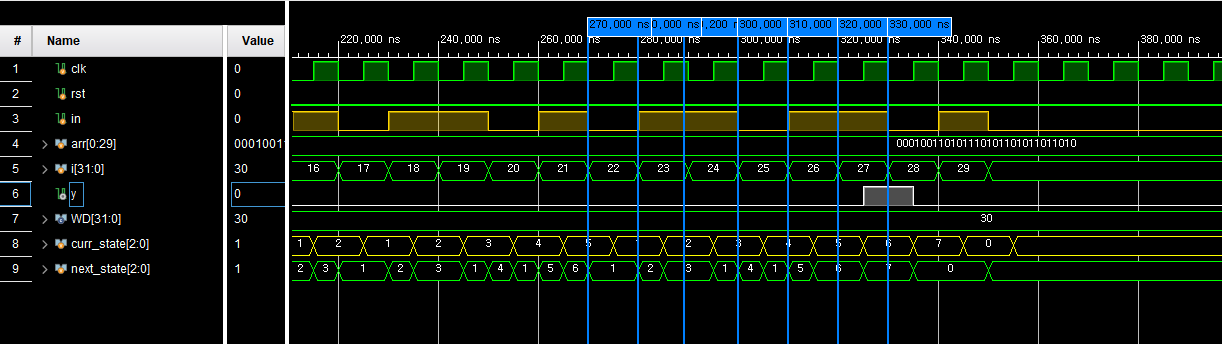
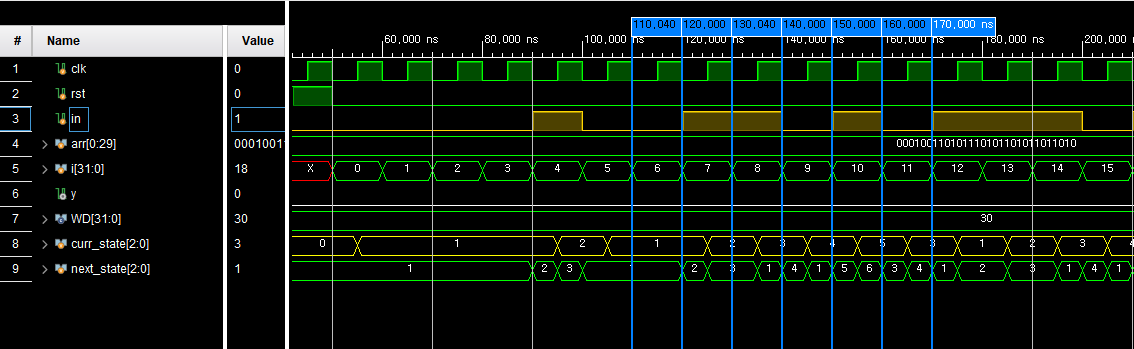
011011이 입력됐을 때는 S7로 넘어가 1이 출력되는 것을 볼 수 있고, 011010이 들어왔을 때는 패턴을 다시 검출해야 하지만, 01이 입력되었기 때문에 S6에서 다음 1을 검출하는 S3으로 천이한 뒤 다시 0이 나오자 S1로 되돌아가는 것을 볼 수 있다.
위 코드는 0110_11_011 과같이 중복된 코드는 잡지 않는다.
module pattern_detect (
input clk, rst, x,
output reg y
);
localparam [3:0] S0 = 3'd0, S1 = 3'd1, S2 = 3'd2, S3 = 3'd3, S4 = 3'd4, S5 = 4'd5, S6 = 4'd6;
reg[2:0] curr_state, next_state;
always @(posedge clk, posedge rst) begin
if(rst) curr_state <= 0;
else curr_state <= next_state;
end
always @(x, curr_state) begin
case (curr_state)
S0 :
if(x) next_state = S0;
else next_state = S1;
S1 :
if(x) next_state = S2;
else next_state = S1;
S2:
if(x) next_state = S3;
else next_state = S1;
S3 :
if(x) next_state = S1;
else next_state = S4;
S4 :
if(x) next_state = S5;
else next_state = S1;
S5 :
if(x) next_state = S6;
else next_state = S3;
S6 : if(x) next_state =S0;
else next_state = S4;
default: next_state = S0;
endcase
end
always @(*) begin
if(next_state == S6) y <= 1'b1;
else y <= 1'b0;
end
endmodule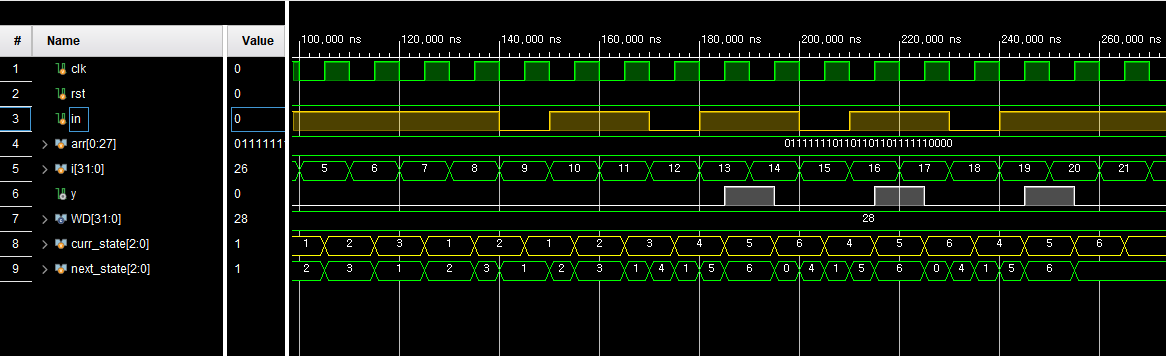
011011_011011 ....을 넣었을 때 중복된 코드로도 패턴을 검출할 수 있게 만들었다.
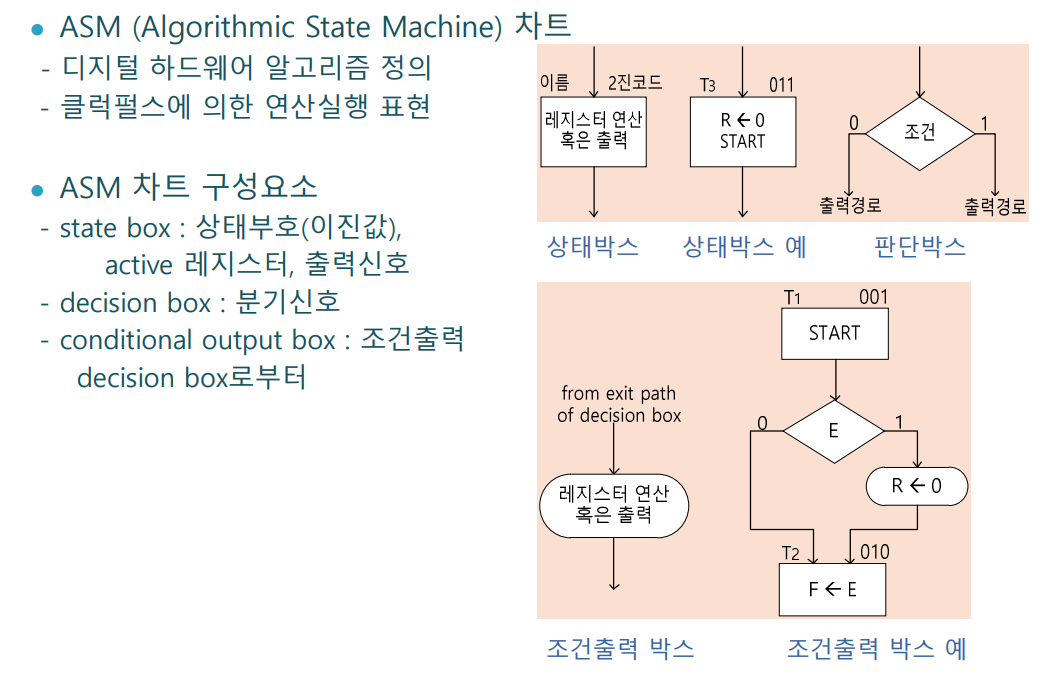
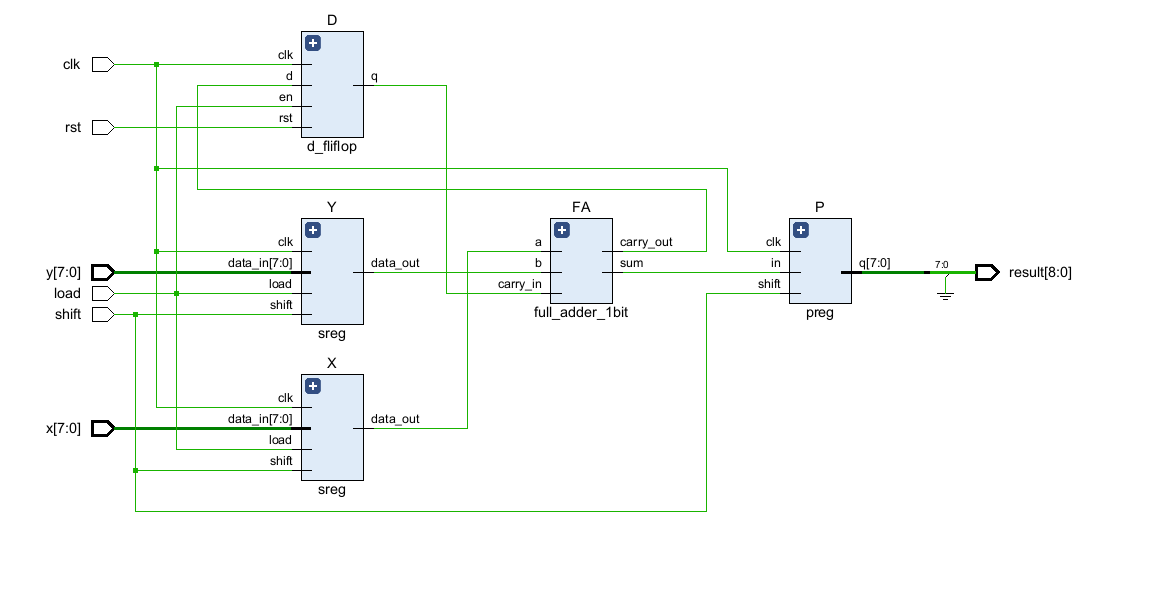
ASM
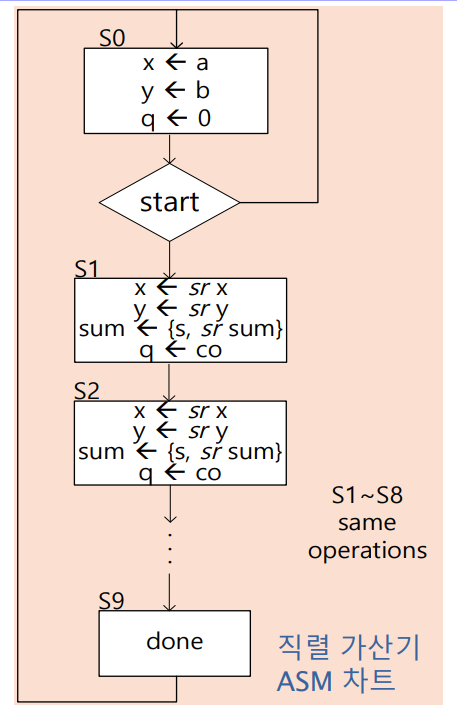
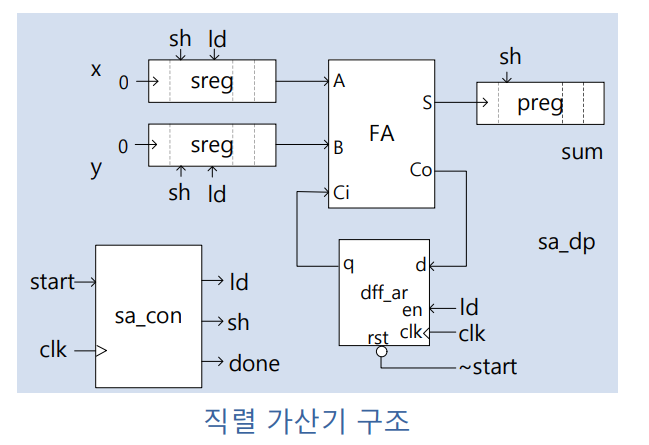
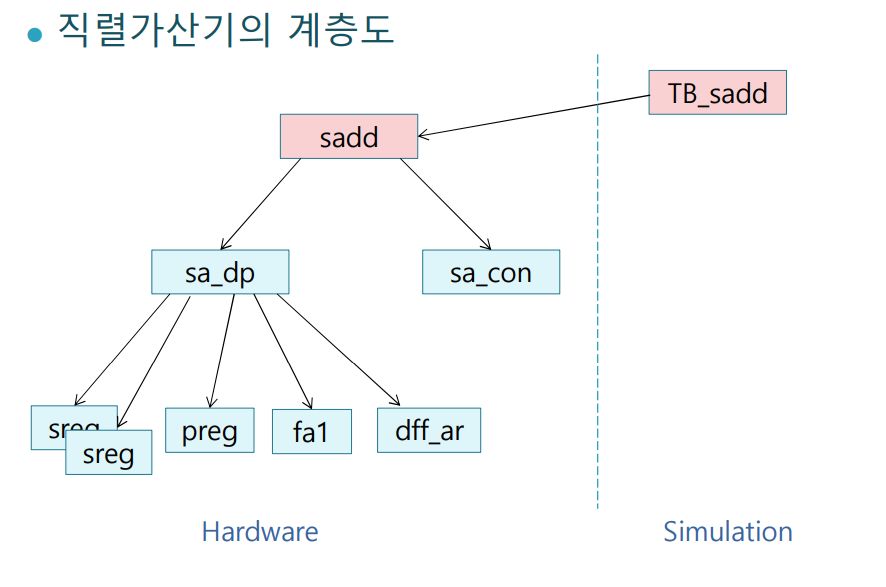
직렬가산기
'Verilog' 카테고리의 다른 글
| verilog 12 cpu설계-2 (0) | 2023.03.27 |
|---|---|
| verilog 11 cpu 제작_1 (0) | 2023.03.20 |
| verilog 9 카운터 실습 (0) | 2023.03.15 |
| verilog7 (0) | 2023.03.14 |
| verilog 5 (0) | 2023.03.13 |